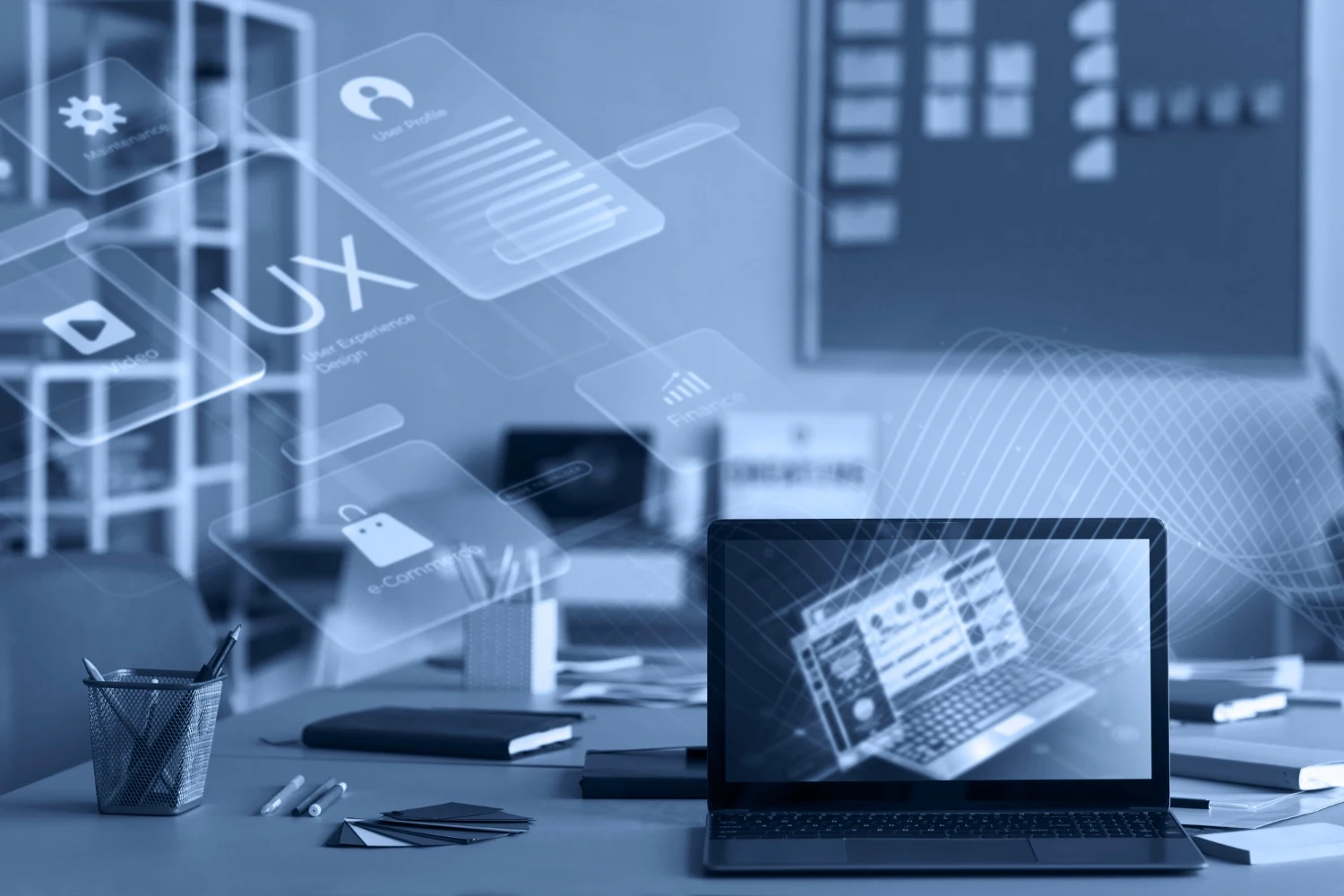
Technological evolution and the growing demand for business efficiency have made the development of integrated software an essential component in the panorama of technological solutions.
These software, designed to interact and communicate with different applications and systems, are increasingly requested in various industrial and commercial sectors.
These are powerful tools that improve the consistency, efficiency and automation of business operations, enabling more seamless and intelligent management of business data and information.
In this article, therefore, we will explore the main characteristics of integrated software, the contexts and sectors in which they are applied, the complete development process and the advantages they can offer to companies.
What are integrated software and where are they applied
THE integrated software, also known as embedded applications or embedded systems, are computer programs designed to interact and communicate bidirectionally with other applications or systems within a larger technological environment.
This type of software is developed to work like a an integral part of an IT ecosystem, enabling interaction, data exchange and synchronization between different applications, platforms or systems.
L'main goal of integrated software is to make company workflows more efficient and coherent, simplifying data management and improving process automation.
To example, an inventory management application can be integrated with an online sales system and a business accounting system. This way, inventory data is automatically synchronized, without the need to manually enter information into each system.
In order for these functions to be guaranteed, therefore, it is necessary that the integrated software have characteristics which:
Interconnection: Embedded software is able to interact with different applications, systems and devices, allowing two-way communication between them.
Data sharing: These software can share data and information between different applications, improving the consistency and accessibility of company information.
Centralization: They are often developed to group and centralize information from different sources, simplifying workflow and data management.
Automation: Integrated software can automate business processes, reducing manual intervention and improving operational efficiency.
Customization: They are designed to be flexible and adapt to specific business needs, allowing a degree of customization to maximize value for the business.
The integrated software, and it seems intuitive given their potential, finds application in different contexts and sectors.
Among these themanufacturing industry, as in the context of industrial production, integrated software manages and controls production processes, the supply chain and logistics.
In healthcare field, such software instead allows the secure sharing of information between facilities, improving the diagnosis and treatment of patients.
They are also used to monitor and optimize the logistics, goods tracking and automation transport.
And again, in financial field, integrated software manages transactions, monitors portfolios and facilitates communication between banks and customers.
Great trend, finally, is the use of integrated software for e-commerce: In this industry, these solutions enable the synchronization of inventory data, orders and payment management.
How integrated software is developed
Embedded software development requires a structured and methodical approach. Nothing should be left to chance.
Developers are often called upon to understand the needs of a specific sector or a single company, so their work must be carried out from scratch every time based on new needs.
For this reason, it is essential that they follow a predefined and essential sequence of fundamental operations for software development.
The main phases, specifically, include:
Requirements analysis: Understand the needs of the business and clearly define the objectives of the integrated software.
Design: Create a detailed software architecture plan, identifying the existing systems with which it will interact.
Development: Write the embedded software code, ensuring that it is compatible with different platforms and systems.
Test and Verification: Conduct extensive testing to ensure correct operation and integration of the software with other systems.
Implementation: Install integrated software into the enterprise environment and provide training and support to users.
Maintenance: Monitor and regularly update the software to ensure its security and efficiency over time.
Attention to Experience and User Interface (UX/UI)
To ensure auser experience (UX) of high quality and auser interface (UI) intuitive, embedded software developers must always keep some fundamental rules in mind.
In fact, designing a user-friendly interface and a smooth experience is essential to maximizing the effectiveness and adoption of the software by users.
A well-designed user interface, combined with a positive user experience, helps make the software more integrated attractive And functional for users, improving the effectiveness and efficiency of business operations.
The first requirement to be satisfied is that the interface is clear and simple to understand, avoiding superfluous elements and information. Users should be able to use the software without having to do research or complex instructions.
There navigation it should then be intuitive, with a logical flow of information and a hierarchical structure that makes it easy to find what users need.
The appearance and behavior of the interface should be coherent throughout the software. Colors, buttons and design elements should follow a uniform style, helping users become familiar with the software.
Of crucial importance is that the interface is responsive, that is, it can adapt to different screen sizes and devices, such as desktop computers, tablets and smartphones, ensuring a pleasant experience on any platform.
Operationally speaking, it would be good for the software to provide a visual feedback immediate when users interact with it. For example, when an action is performed, the software should provide a message or animation that confirms the completion of the action.
Another aspect to take into consideration is the ease of input, minimizing the amount of data required from users, favoring techniques such as auto-completion and guided selection to simplify typing.
From a graphic point of view, however, the icons and images used in the interface should be easily recognisable and representative of the actions or functions to which they refer.
Whenever possible, it would also be very functional to allow users to customize the interface based on their preferences, for example by allowing them to choose the layout of the panels or the colors.
An essential element is that of safety. Especially if the software requires access to sensitive data, it is important to ensure that the interface is protected and that adequate security measures are in place.
If all the features weren't enough to guarantee a completely intuitive experience, it would be a good idea to provide easy access to support resources, such as guides, tutorials or a built-in help system, to help users better understand the software and resolve any problems.
Finally, the developers' task does not stop at the creation of the software.
The last step is to conduct usability tests with target users to identify any problems or difficulties in interacting with the software, using user feedback to make continuous improvements.
Advantages for Companies
The application of integrated software offers numerous advantages to companies, first of all that of obtaining a operational efficiency markedly improved.
System integration, in fact, reduces the duplication of information and automates processes, improving overall efficiency.
Access to centralized and timely data then helps managers to make informed decisions and strategic, thanks to data analysis tools with high predictive potential.
But process automation also means reduction of the risk of errors humans, increasing the reliability of business operations.
Integrated software, it is absolutely not to be underestimated, is designed to be scalable and to grow with the company, allowing you to adapt to expanding business needs and sudden market changes.
The key word in all of this is competitiveness.
This is the reason why companies want to rely on software solutions of this type, and this is always the reason that drives them to invest in innovation.
Embedded software plays a crucial role in supporting business efficiency and automation, enabling a smoother workflow it's a better information management.
Noitech revolutionizes your digital efficiency
Their ability to interconnect with different applications and systems makes integrated software a tool capable of offering companies a competitive advantage unique.
In Noitech we know it, and we are expert innovators specializing in development of solutions for different integrated systems in various industries.
Our highly qualified team has deep industry knowledge and provides invaluable support to businesses looking to stay ahead of the curve.
Our expert consultants in fact, they work closely with customers to provide comprehensive assistance based on technological requirements and industry standards.
If you need a reliable partner to navigate the latest trends or a customized, cutting-edge solution, Noitech is the right choice.
With our experience in software development, we customize solutions to meet your business needs and we revolutionize your digital efficiency.
Contact us without hesitation for any curiosity about the digital services we offer and to enter the world of Noitech-branded innovation.