The development of collaborative robotics has now redefined the relationship between man and machine.
A paradigm that involves close cooperation between robotic systems and human work, also allowing physical interaction in confined spaces.
However, it must be highlighted that there are no "collaborative" machines by nature. A robot may indeed be designed for a collaborative task, but it is the application that does all the work.
It is the application that makes the robot "collaborative".
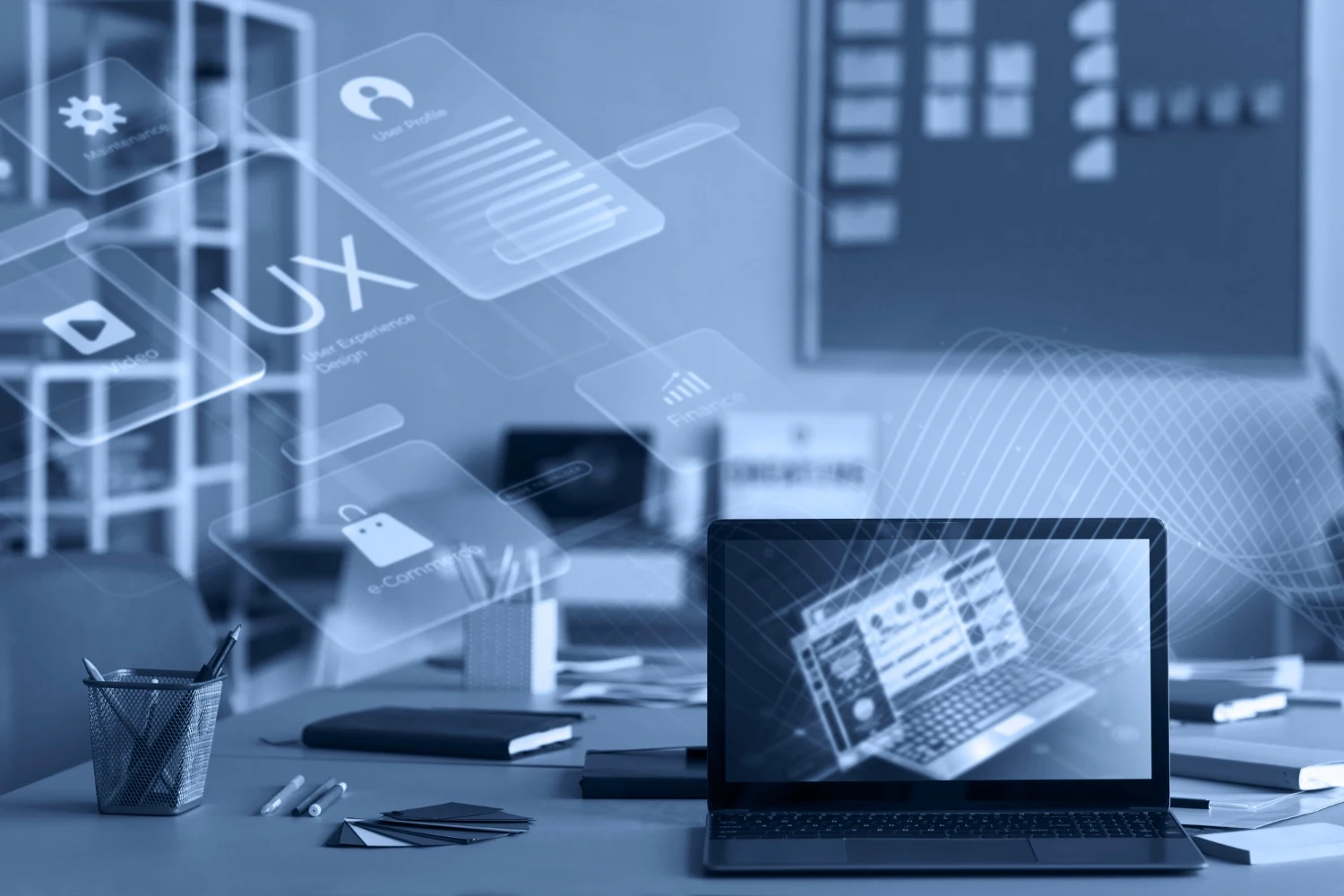
A fundamental role, in this situation, is played byartificial intelligence which therefore, also in application to collaborative robotics, is among the enabling technologies of Industry 4.0.
AI and differences between traditional robots and Cobots
It is precisely artificial intelligence that allows, therefore, the creation of intelligent machines capable of working and reacting like human beings, as well as interacting with them.
The management of collaborative robots (Cobots) is also made easier by their ability to acquire information, to be able to interpret the world around them and decide what action to take.
This is the concept behind the Machine Learning, a branch of artificial intelligence based on automatic learning by machines.
Thanks to AI, ultimately, users are no longer required to know software or programming languages, but simply show the robot what it has to do.
To this, there are three big differences between the so-called "traditional" robots and the Cobots;
- Flexibility: Lightweight and small in size, Cobots can also operate in small spaces and, if they are moved, they can be easily reprogrammed.
- Ready for use: Since Cobots do not require complex changes to production schemes, they can be implemented very quickly and can be quickly integrated into work areas.
- Safety: Cobots, unlike traditional robots, can operate without the use of protective barriers or cages. They can also be equipped with a series of sensors and viewers which increase operational effectiveness and safety
Precisely the latter is the case of 3D viewer with AI on Board, patented by Noitech and mounted on the mobot/Cobot todrobot TR1.
Collaborative robotics and physical human-robot interaction
There collaborative robotics It therefore allows safe physical interaction with humans.
Cobots, sharing space with human operators, have opened the way to a different way of using robotics in the industrial sector and beyond.
In the'physical human-robot interaction (PhHRI, or Physical Human-Robot Interaction), the aspects of perception of the environment and prediction of human intention represent a fundamental requirement.
And this is how the human-robot combination produces benefits in a twofold direction:
- Man can be relieved by heavy operations, as the transfer and manipulation of heavy loads, the execution of repetitive and demanding tasks, etc.;
- The robot can benefit from the individual abilities of humans, able to predict and resolve imprecise situations, to adapt to the flexibility and variability of tasks.
The challenges of AI for collaborative robotics
The challenges facing artificial intelligence were discussed during a conference, organized by Siri (Italian Association of Robotics and Automation), on the occasion of 33rd edition of BiMu.
What stands out is the one about the perception of the environment, or the robot's ability to plan and make decisions autonomously.
Over the last 10 years, with the explosion of Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Computer Vision, artificial intelligence has made great strides.
The improvements achieved in the field of artificial vision, above all, they allow machines today to interpret even very complex situations. All this made it possible to enable that cycle of perception, reasoning and action, necessary for carrying out increasingly complicated tasks and perfecting human-machine interaction.
The challenge launched by BiMu is to go beyond the current level of interaction, to obtain automation that sees the robot carry out tasks autonomously.
The arrival point is what is called "human in the execution loop", where humans and robots work in the same environment, but without sharing at a decision-making level.
To address these challenges, as stated by Domenico Appendino, President of Siri, we need to promote collaboration between the academic and industrial worlds «which in our country often still travel on two separate tracks».
A mantra, this, that Noitech has always made it his own. It is in fact right from In House Research and Development department, composed of academics and engineers, where our advanced technological solutions are born.